Understanding VXLAN
Understanding VXLAN: Virtual Extensible LAN
Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) is a network virtualization technology that helps extend Layer 2 networks over Layer 3 infrastructure. It’s a key enabler in modern data centers, especially in cloud environments, providing scalable overlay networks for virtual machines and containers.
1. What is VXLAN?
VXLAN is a network overlay protocol that allows you to create a virtual Layer 2 network over a physical Layer 3 network. It encapsulates Ethernet frames in UDP packets, enabling the deployment of virtual networks across large, distributed environments.
- VXLAN Header: Encapsulates the original Ethernet frame.
- UDP Encapsulation: Uses UDP for transport over Layer 3 networks.
- VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI): A 24-bit ID allowing up to 16 million unique VXLAN segments.
What does VXLAN look like?
IP Packet
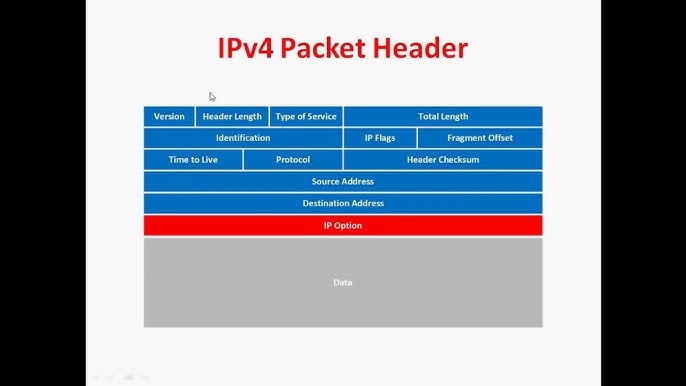
VXLAN Packet
2. Why VXLAN?
Traditional VLANs are limited to 4096 VLAN IDs, which restricts scalability, especially in large cloud or multi-tenant environments. VXLAN solves this issue by providing 16 million unique VXLAN IDs (VNIs).
Benefits of VXLAN:
- Scalability: Supports millions of unique network segments.
- Flexibility: Works over existing Layer 3 networks.
- Mobility: Enables seamless VM and container movement between hosts.
- Multi-Tenant Isolation: Provides network segmentation for tenants in cloud environments.
3. How VXLAN Works
VXLAN works by encapsulating Layer 2 frames inside Layer 3 packets using UDP encapsulation. This enables the transport of Ethernet frames over IP networks.
- Encapsulation: Ethernet frames are encapsulated into UDP packets.
- Routing: These UDP packets are routed over the existing Layer 3 network.
- Decapsulation: At the destination, the original Ethernet frame is extracted.
4. VXLAN Components
VTEP (VXLAN Tunnel Endpoint):
- Handles encapsulation and decapsulation of Ethernet frames.
- Each host in a VXLAN environment requires a VTEP.
VNI (VXLAN Network Identifier):
- A unique 24-bit identifier for VXLAN segments, supporting up to 16 million segments.
Flood and Learn:
- VXLAN relies on multicast or control-plane protocols (like EVPN) to handle Layer 2 broadcasts and MAC address learning.
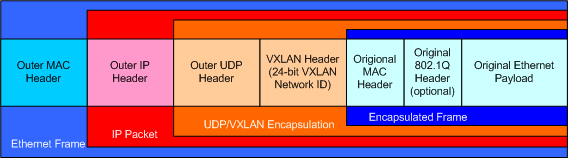
5. VXLAN Packet Format
A VXLAN packet contains the following headers:
- Ethernet Header (Original Layer 2 frame)
- VXLAN Header (Includes VNI)
- UDP Header (Transport over Layer 3)
- IP Header (Routing information for Layer 3)
- Ethernet Header (Outer Ethernet header)
6. VXLAN vs VLAN
| Feature | VLAN | VXLAN |
|---|---|---|
| ID Limit | 4096 VLANs | 16 million VNIs |
| Layer | Layer 2 | Layer 2 over Layer 3 |
| Encapsulation | None | UDP encapsulation of Ethernet |
| Use Case | Small to medium-sized networks | Large, distributed environments |
7. Use Cases of VXLAN
- Cloud Data Centers:
- VXLAN allows multiple tenants to operate isolated networks on shared infrastructure.
- Kubernetes Networking:
- VXLAN is used in CNI plugins like Calico or Flannel to manage pod networking across nodes.
- Virtual Machine Migration:
- Ensures seamless connectivity when VMs are moved across different physical hosts.
8. Configuring VXLAN with Linux
You can create a VXLAN interface on Linux using the following commands:
Step 1: Create a VXLAN Interface
ip link add vxlan0 type vxlan id 42 dev eth0 dstport 4789
Step 2: Assign an IP Address
ip addr add 192.168.100.1/24 dev vxlan0
Step 3: Bring Up the Interface
ip link set vxlan0 up
9. VXLAN in Kubernetes (Example with Flannel)
Many CNI plugins in Kubernetes, such as Flannel, use VXLAN to provide network connectivity between pods across nodes.
Flannel Configuration Example:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: flannel-vxlan-config spec: backend: vxlanBenefit:
- Pods can communicate seamlessly across nodes by leveraging VXLAN-based networking.
10. Troubleshooting VXLAN
Here are a few commands to diagnose and troubleshoot VXLAN issues:
Check VXLAN Interface:
ip link show vxlan0Check Routing Table:
ip route showCapture VXLAN Traffic (using
tcpdump):tcpdump -i eth0 udp port 4789
11. Security Considerations
While VXLAN provides network segmentation, it’s important to consider:
- Encryption: VXLAN itself doesn’t provide encryption. Use IPsec or TLS to secure traffic.
- Control Plane Security: Protect control plane protocols like EVPN from unauthorized access.
12. Conclusion
VXLAN plays a critical role in network virtualization, enabling scalable and flexible networking in cloud and data center environments. Whether you’re working with Kubernetes, virtual machines, or multi-tenant networks, understanding VXLAN is essential for modern network engineers.
Next Steps
Interested in more networking topics? Check out these related posts: