RKE2: A Deep Dive into CNI options
Table of Contents
RKE2’s CNI Options: Canal, Cilium, Calico, and Multus
RKE2, also known as Rancher Kubernetes Engine 2, is a CNCF-certified Kubernetes distribution that simplifies the deployment and management of Kubernetes clusters. One of the critical components of any Kubernetes cluster is the Container Network Interface (CNI), which facilitates inter-pod communication and network policy enforcement. In this post, we’ll explore the CNI options available in RKE2: Canal, Cilium, Calico, and Multus, and help you understand which might be the best fit for your needs.
Canal: The Best of Flannel and Calico
Canal is a CNI provider that combines Flannel’s simple overlay networking capabilities with Calico’s network policy enforcement. It’s designed to be easy to set up and maintain, offering a good balance between performance and features.
Canal Key Features
- Overlay Networking: Uses Flannel for efficient data plane operations.
- Network Policies: Integrates Calico’s advanced network policy management.
- Simplicity: Ideal for those who want a straightforward setup without sacrificing security features.
Canal Installation
# /var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/manifests/rke2-canal-config.yaml
---
apiVersion: helm.cattle.io/v1
kind: HelmChartConfig
metadata:
name: rke2-canal
namespace: kube-system
spec:
valuesContent: |-
flannel:
iface: "eth1"
How Canal works
Canal uses Flannel to manage the overlay network that allows pods to communicate across different nodes. Flannel assigns a unique subnet to each node, reducing the complexity of network management. Calico’s role in Canal is to enforce network policies, which it does by implementing a virtual network that controls packet flow between pods based on rules defined in Kubernetes NetworkPolicy objects.
The basic idea is that Flannel uses VXLAN to encapsulate packets when sending packets outside the current node. Then, the packets are decapsulated by the destination node. Then, each node is assigned a subnet, default is /24, out of the cluster-cidr. Then flannels static routes to direct traffic to the correct node.
The following diagram illustrates how the Canal works:
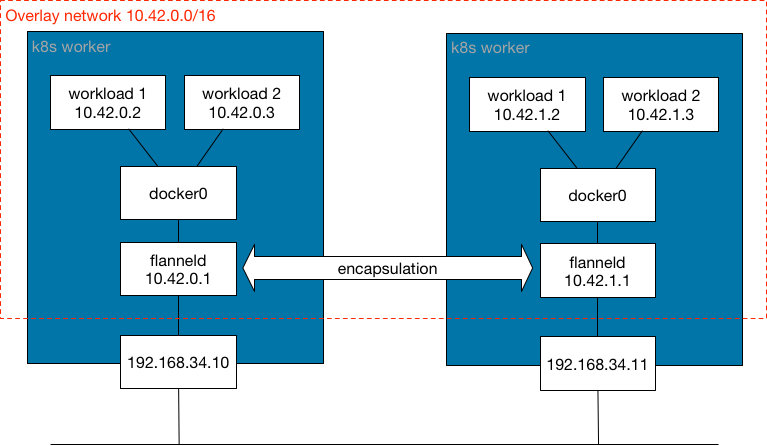
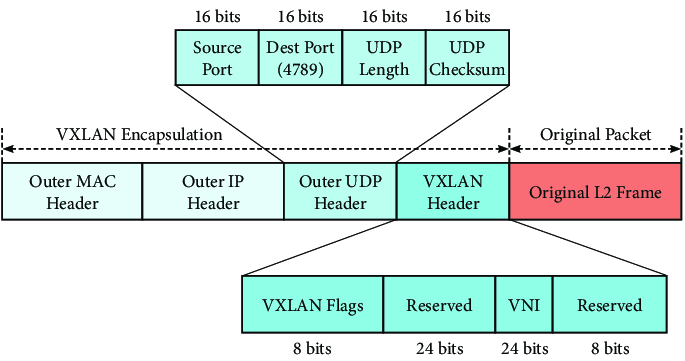
Canal Troubleshooting
- Canal Troubleshooting
- Canal Troubleshooting: Flannel
- Increase log level for Canal
- Flannel troubleshooting documentation
Canal Offical Links
Cilium: Advanced Security with eBPF
Cilium is a cutting-edge CNI option that leverages eBPF to provide highly scalable and secure networking. It’s particularly well-suited for environments that require stringent security measures and deep visibility into network flows.
Cilium Key Features
- eBPF-Based: Offers high performance and security.
- Security: Provides robust security features, including encryption and policy enforcement.
- Visibility: Enables detailed monitoring and troubleshooting capabilities.
Cilium Installation
# /var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/manifests/rke2-cilium-config.yaml
---
apiVersion: helm.cattle.io/v1
kind: HelmChartConfig
metadata:
name: rke2-cilium
namespace: kube-system
spec:
valuesContent: |-
eni:
enabled: true
How Cilium works
Cilium operates at the Linux kernel level using eBPF technology. eBPF allows it to dynamically insert and compile security policies into the kernel without changing kernel source code or loading kernel modules. Cilium provides API-aware network security and visibility by placing eBPF loaders at strategic points in the network stack to make intelligent routing and security decisions.
The following diagram illustrates how Cilium works:
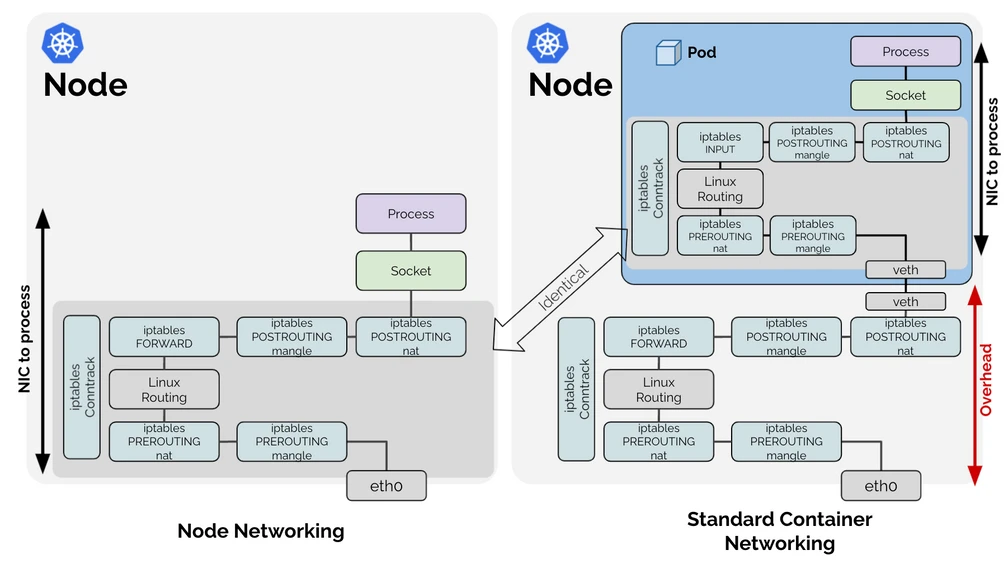
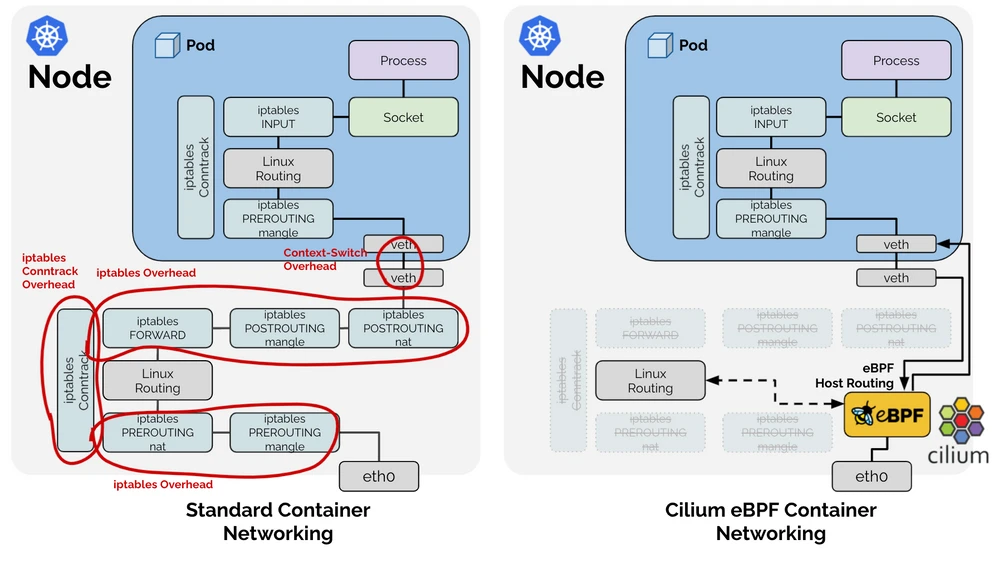
Cilium Troubleshooting
Cilium Offical Links
Calico: Fine-Grained Network Policies
Calico is known for its fine-grained network policy enforcement, which makes it a popular choice for enterprises that need precise control over their network traffic.
Calico Key Features
- Network Policies: Supports complex network policy configurations.
- Performance: Designed for high-performance environments with native support for various networking options.
- Flexibility: Can be used with or without an overlay network, depending on the performance requirements.
Calico Installation
# /var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/manifests/rke2-calico-config.yaml
---
apiVersion: helm.cattle.io/v1
kind: HelmChartConfig
metadata:
name: rke2-calico
namespace: kube-system
spec:
valuesContent: |-
installation:
calicoNetwork:
mtu: 9000
How Calico works
Calico uses a pure Layer 3 approach to networking for pods. It assigns an IP address to each pod and uses IP routing to deliver packets to their destinations. This approach avoids overlay networks and NAT, providing high performance and lower latency. Calico also implements fine-grained network policies using iptables rules applied to the host’s Linux kernel.
The following diagram illustrates how Calico works:
Calico Troubleshooting
Calico Offical Links
Multus: The Multi-Network Swiss Army Knife
Multus is a meta-CNI plugin that allows a pod to have multiple network interfaces. It’s an excellent option for workloads that need to be connected to different networks simultaneously.
Multus Key Features
- Multi-Network: Supports attaching multiple network interfaces to pods.
- Flexibility: Works with any CNI-compliant plugin, providing a wide range of networking options.
- Use Cases: Ideal for advanced use cases like NFV, multi-tenancy, and hybrid cloud setups.
Multus Installation
# /var/lib/rancher/rke2/server/manifests/rke2-cilium-config.yaml
---
apiVersion: helm.cattle.io/v1
kind: HelmChartConfig
metadata:
name: rke2-cilium
namespace: kube-system
spec:
valuesContent: |-
cni:
exclusive: false
How Multus works
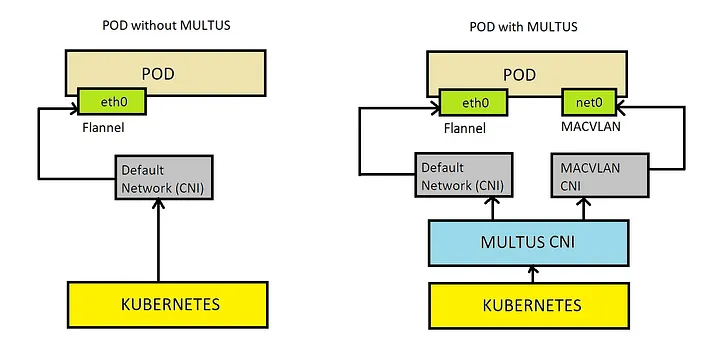
Multus acts as a “meta-plugin” that allows a pod to be attached to multiple networks. It works with the primary CNI plugin to provide additional pod interfaces. Multus adheres to the CNI specification and can support any CNI-compliant plugin, enabling the pod to communicate with different networks. This can be especially useful in advanced networking scenarios like network function virtualization (NFV).
It’s important to understand that for traffic that comes through Kubernetes services or ingress resources, the primary network interface is typically used. The second network is only used if the pod directly reaches out using the second network interface. IE, you must make the application aware of the second network interface. NOTE: Longhorn supports Multus to force storage traffic to use the second network interface.
The following diagram illustrates how Multus works:
Multus Troubleshooting
TBD
Multus Offical Links
Conclusion
Choosing the right CNI for your RKE2 cluster depends on your specific use case and requirements. Whether you prioritize ease of use, security, performance, or flexibility, RKE2 offers a range of CNIs to fit your needs. By understanding the strengths of Canal, Cilium, Calico, and Multus, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your operational objectives.
For more detailed information on each CNI option, refer to the official RKE2 documentation or contact the community for support.
