Kube-VIP as TCP/UDP Load Balancer for RKE2

This guide explains how to set up Kube-VIP as a Layer2 TCP/UDP load balancer for an RKE2 cluster.
For details on configuring ingress within RKE2, refer to the Ingress NGINX Controller on RKE2 Guide.
Overview
What is Kube-VIP?
Kube-VIP is a lightweight virtual IP (VIP) manager that provides TCP/UDP load balancing and virtual IPs for Kubernetes clusters. In Layer2 mode, Kube-VIP broadcasts ARP packets to associate a VIP with the active Kubernetes node.
Key Features
- Layer2 ARP-Based VIP Management: Ideal for bare-metal and on-prem environments.
- Built-in TCP/UDP Load Balancer: Provides load balancing for Kubernetes services.
- High Availability: Ensures failover between nodes for VIPs.
For more details, visit the Kube-VIP Documentation.
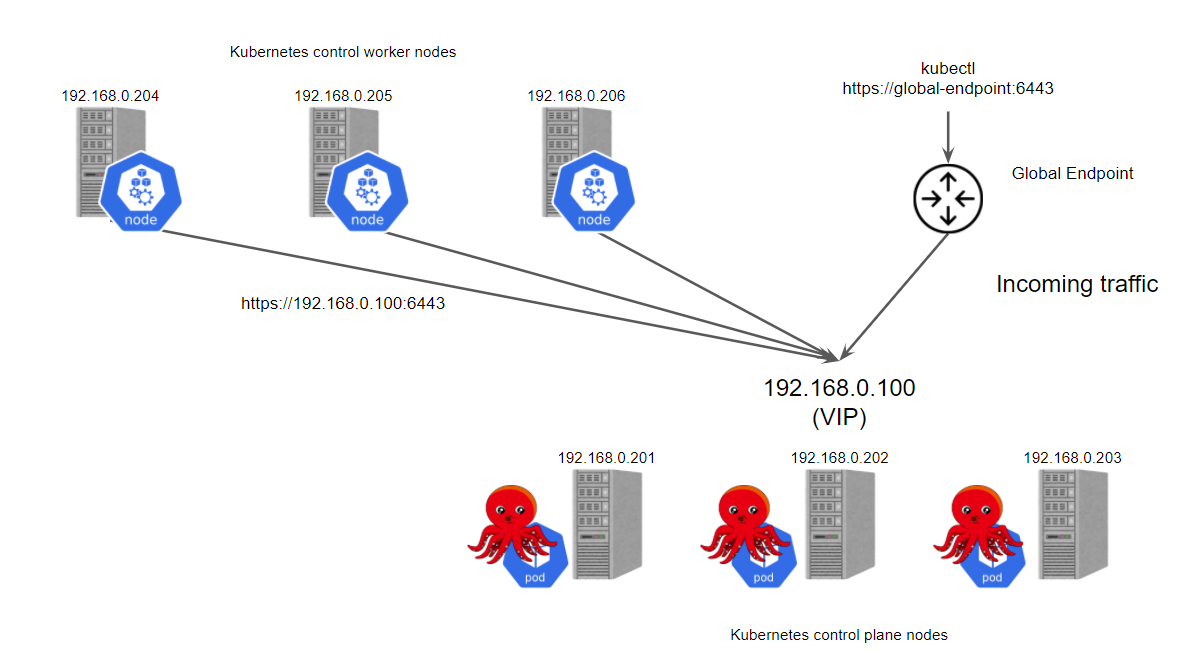
Setup Instructions
Step 1: Install Kube-VIP
Deploy the Kube-VIP Manifest:
kubectl apply -f https://kube-vip.io/manifests/kube-vip.yamlVerify the Installation: Ensure that the
kube-vippod is running in thekube-systemnamespace:kubectl get pods -n kube-system -l app=kube-vip
Step 2: Configure the Kube-VIP ConfigMap
Example: Static VIP Configuration
Edit the ConfigMap: Retrieve and edit the Kube-VIP ConfigMap:
kubectl -n kube-system edit configmap kube-vipSet Layer2 Configuration: Add the following configuration under the
datasection:apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: kube-vip namespace: kube-system data: vipAddress: "192.168.1.100" # Replace with your desired VIP vipSubnet: "255.255.255.0" enableARP: "true" loadBalancers: - name: rke2-api type: tcp vip: "192.168.1.100" ports: - port: 6443 backends: - address: "192.168.1.101" # Replace with control-plane node IPs port: 6443 - address: "192.168.1.102" port: 6443
Example: DHCP Configuration
- Edit the ConfigMap:
If you prefer to use DHCP to obtain the VIP, modify the
ConfigMapas follows:apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: kube-vip namespace: kube-system data: enableARP: "true" enableDHCP: "true" loadBalancers: - name: rke2-api type: tcp vip: "dhcp" ports: - port: 6443 backends: - address: "192.168.1.101" port: 6443 - address: "192.168.1.102" port: 6443
Step 3: Test the VIP
Validate ARP Entries: Check ARP entries on another machine in the same network:
arp -a | grep 192.168.1.100Test Connectivity: Verify that the VIP forwards traffic to the RKE2 control plane:
curl -k https://192.168.1.100:6443
Deploying Kube-VIP via ArgoCD
For environments leveraging ArgoCD for GitOps, you can deploy Kube-VIP with the following manifest:
ArgoCD Application Manifest
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: kube-vip
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: kube-system
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: load-balancers
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/kube-vip/kube-vip
targetRevision: v0.5.0
path: manifests
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
Customizing Load Balancers
Kube-VIP supports custom TCP/UDP load balancer configurations. For example, to add an HTTP(S) load balancer for ingress traffic:
Example ConfigMap Entry for Ingress Traffic
loadBalancers:
- name: ingress-http
type: tcp
vip: "192.168.1.200"
ports:
- port: 80
backends:
- address: "192.168.1.103" # Replace with ingress node IPs
port: 80
- address: "192.168.1.104"
port: 80
- name: ingress-https
type: tcp
vip: "192.168.1.200"
ports:
- port: 443
backends:
- address: "192.168.1.103"
port: 443
- address: "192.168.1.104"
port: 443
Integration with RKE2
Kube-VIP integrates seamlessly with RKE2 clusters to provide load balancing for Kubernetes services, including the control plane and ingress traffic. For more details, refer to the Ingress NGINX Controller on RKE2 Guide.